Exercise
1-1: Glo Germ Hand Washing Education
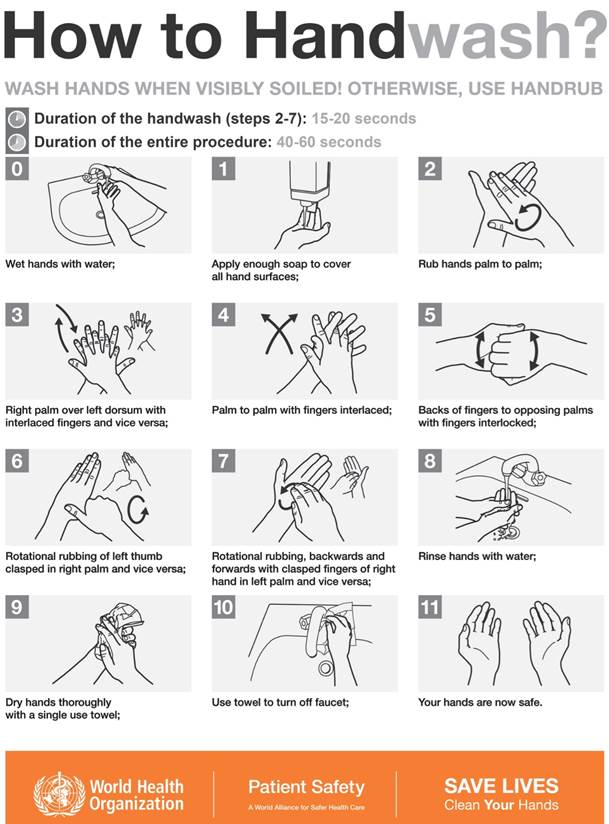
Hand Washing Lab
Antimicrobial – destroying or inhibiting the growth of microorganisms
and especially pathogenic microorganisms.
Efficacy - capable of having the desired result or effect;
effective as a means, measure, remedy, etc.
Floral
bacterial – Microorganisms including bacteria, protozoa, and fungi that are normally found on
or in specific areas of the body. They do not cause disease under normal
circumstances. These are sometimes referred to as resident bacteria.
Germs – a microorganism, especially one that causes disease.
Microbes – archaea, bacteria, fungi, viruses. Microbes are single-cell organisms so tiny that millions
can fit into the eye of a needle. Usually referring to a bacterium
causing disease or fermentation.
Triclosan – an antibacterial and antifungal agent found in consumer products,
including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments.
Transient
bacteria – temporary skin flora
refers to the microorganisms that transiently colonize the skin.
This includes bacteria,
fungi and viruses, which reach the hands, for example, by direct skin-to-skin
contact or indirectly via objects. They are sometimes called contaminant bacteria.
How we
pick up bacteria:
·
Food
borne – A disease caused by
consuming contaminated and
spoiled food or drink. There are more than 250 known foodborne diseases. The majority are
infectious and are caused by bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Other foodborne diseases are essentially poisonings caused by toxins,
chemicals contaminating the food.
·
Indirect
transmission – a transmission mechanism in which the infectious
agent is transferred to the person by a fomite of vector.
o
Fomite
–
an object (as a dish or a doorknob) that may be
contaminated with infectious organisms and serve in their transmission.
o
Vector
–
an organism, typically a biting insect or tick, that transmits a disease or parasite from one animal
or plant to another.
·
Person-to-person
transmission –the most common form of transmitting diseases
and virus. There are two types of contact transmission: direct and indirect.
o
Direct contact transmission occurs when there
is physical contact between an infected person and a susceptible person. Disease-causing
microorganisms pass from the infected person to the healthy person via direct
physical contact with blood or body fluids.
o
Indirect contact transmission occurs when there
is no direct human-to-human contact. Indirect contact infections spread when an
infected person sneezes or coughs, sending infectious droplets into the air. If
healthy people inhale the infectious droplets, or if the contaminated droplets
land directly in their eyes, nose or mouth, they risk becoming ill.
·
Water
borne transmission –any illness
caused by drinking water contaminated by human or animal feces,
which contain pathogenic microorganisms. Infection commonly results during bathing, washing,
drinking, in the preparation of food, or the consumption of food that is
infected.
The recommended time for hand washing, to remove transient microbes, is
15 to 20 seconds. Surgical scrubs last for 5 minutes.
Exercise 1-2:
A Comparison of Hand-Cleansing Agents
Procedure:
1. Use an assigned hand-cleansing agent
2. Label the bottom side (agar side) of your petri dish as seen below:
a. ***Be sure to write your name and which
hand-cleansing agent you used on your petri dish!***
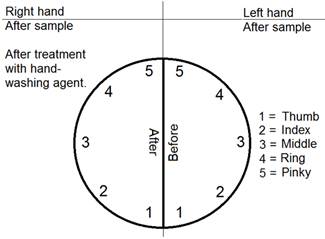
3. Rub your left hand’s finger tips (all 5 of them) on a sample area known to be contaminated with bacteria (the floor, the soles of your shoes, a tabletop near a sink, your backpack, your forehead, or your feet, etc.)
4. One at a time, gently press your fingertips into the “Before” spots on your petri dish.
5. Wash your hands with soap and water.
6. Now, sample the same site with your right hand, but only one fingertip at a time. Then rub that fingertip in the hand-cleansing agent in your left palm for 10 seconds (follow the directions on the bottle whether you need to air dry or rinse with water and dry).
7. Once the fingertip is dry, gently press it into the “After” side of the petri dish.
8. Repeat steps 6 & 7 until you have done all fingertips on the right hand.
9. Incubate the dish. We will observe results next week.